Understanding Vector Databases: A Comparative Guide with Traditional Databases
Vector databases, designed for AI applications, contrast traditional databases with their dynamic organization and nuanced retrieval
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of technology, databases have always been the cornerstone of information storage and retrieval. As we delve deeper into the realms of artificial intelligence and machine learning, the need for specialized databases becomes paramount. Enter Vector Databases—a new breed of databases tailored for the modern age. But how do they stack up against the traditional databases we've grown accustomed to? Let's embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of vector databases in comparison to their traditional counterparts.
1. Basics & Definitions
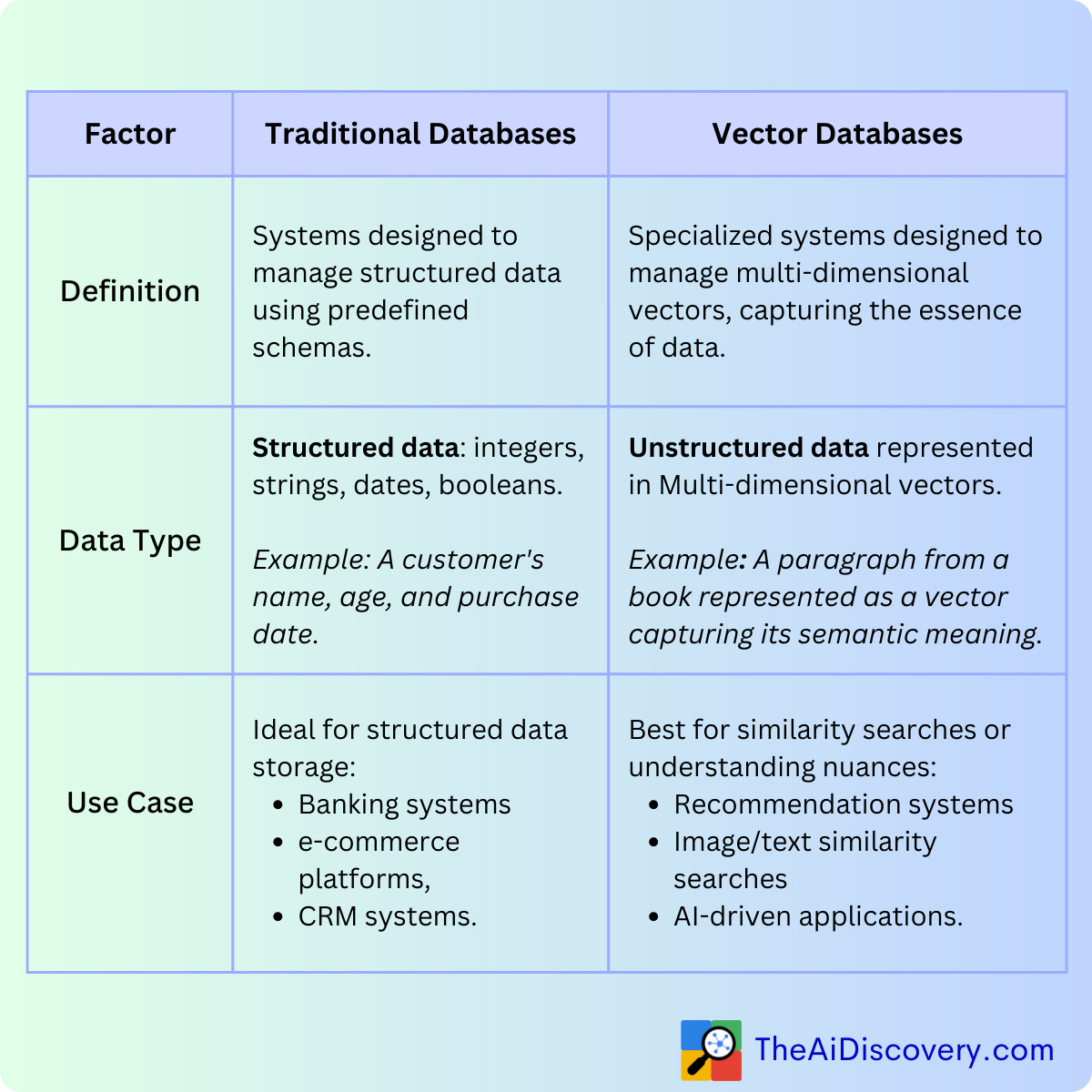
Traditional Databases have been the backbone of countless applications, providing a structured way to store and retrieve data. They are systems designed to manage structured data using predefined schemas, making them ideal for applications like banking systems, e-commerce platforms, and CRM systems.
On the other hand, Vector Databases are the new kids on the block, designed to manage multi-dimensional vectors that capture the essence of data. These vectors can represent anything from a paragraph in a book to the features of an image, making them invaluable for applications that rely on similarity searches or understanding the nuances in data.
2. Data Organization & Structure
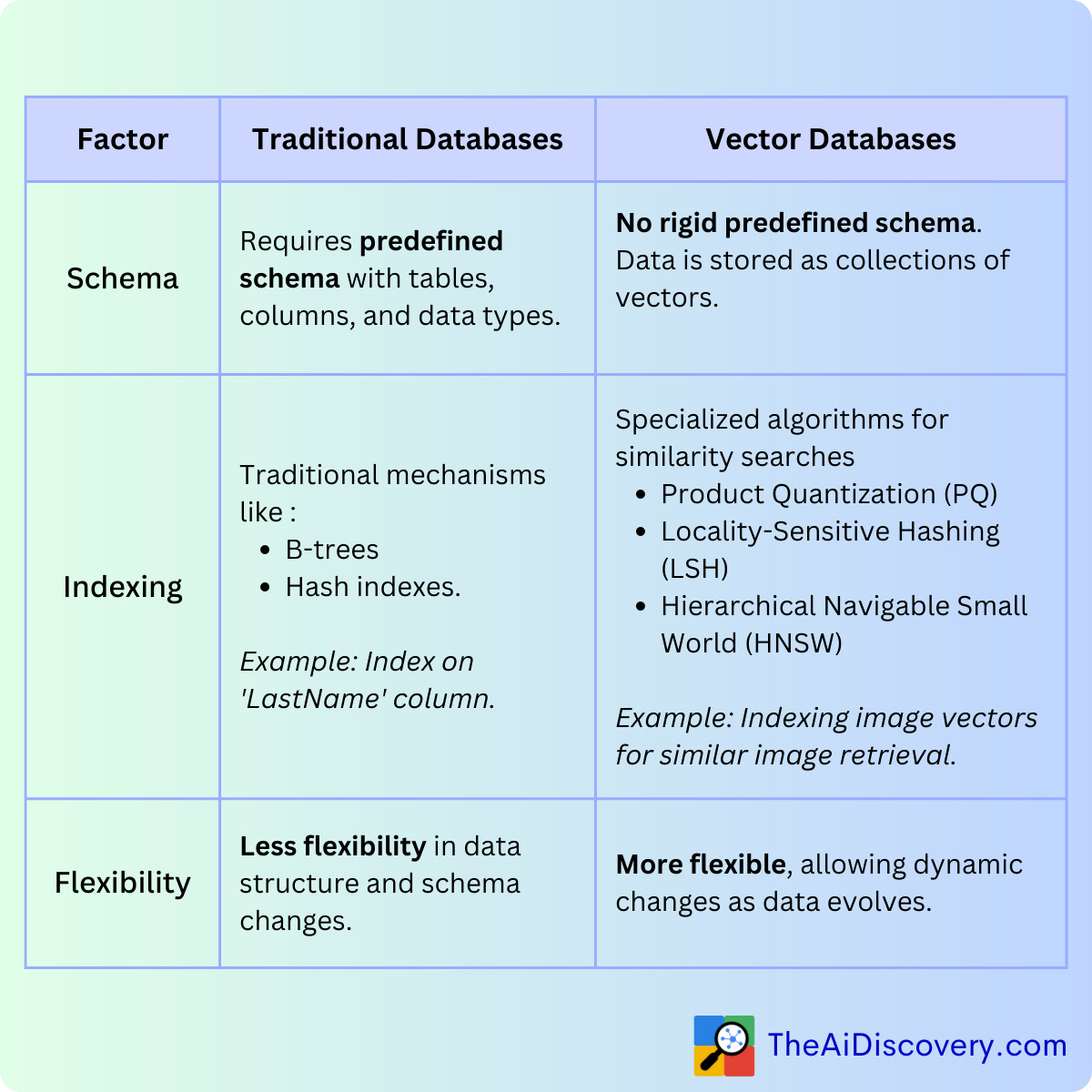
The way data is organized and structured is fundamental to how a database operates. Traditional Databases rely on a predefined schema, organizing data into tables with specific columns and data types. This rigid structure, while reliable, offers less flexibility when it comes to evolving data needs.
Vector Databases, in contrast, do not rely on such rigid schemas. They store data as collections of vectors, which can vary in dimensions and types. This flexibility allows them to adapt dynamically as the nature of the data evolves, making them particularly suited for diverse and evolving datasets.
3. Operations & Performance
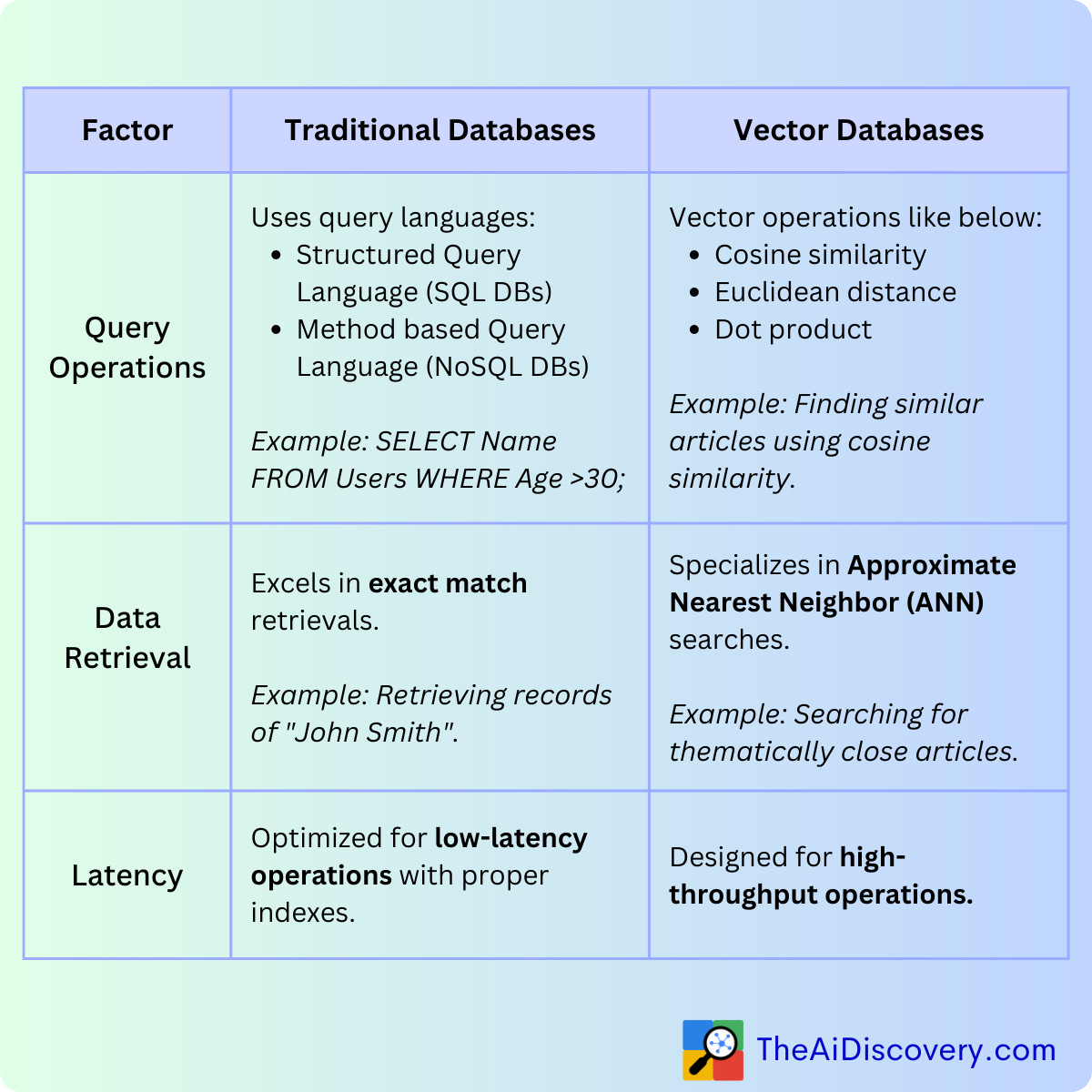
When it comes to the nitty-gritty of operations, Traditional Databases use SQL or specific query languages. They excel in exact match retrievals, providing precise results quickly when the right indexes are in place.
Vector Databases operate differently. Instead of SQL, they leverage vector operations, such as dot product and cosine similarity, to retrieve data. Their strength lies in approximate nearest neighbour (ANN) searches, finding vectors that are 'close' or 'similar' to a given vector. This makes them indispensable for tasks like recommendation systems or semantic searches.
4. Ecosystem & Management
No database operates in isolation. The ecosystem and management tools surrounding a database play a crucial role in its adoption and efficiency. Traditional Databases come with a mature ecosystem, boasting tools for monitoring, backup, replication, and more. Their security features, honed over years, include access controls, encryption, and audit trails.
Vector Databases, being relatively newer, are still building their ecosystem. However, with their increasing adoption, tools and security features are rapidly evolving. Their storage mechanisms often employ a hybrid approach, leveraging both in-memory and disk-based storage for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Vector databases, with their unique approach to data storage and retrieval, signify the next step in the evolution of databases. While traditional databases remain foundational for many applications, the rise of AI and machine learning underscores the importance of databases that can understand nuances and similarities in data. As we stand at this crossroads, understanding the strengths and capabilities of each database type is crucial. Whether you're a developer, a data scientist, or just a tech enthusiast, the world of vector databases offers a glimpse into the future of technology, and it's a future full of promise.